Google Cloud SQL (MySQL)

Cloud SQL MySQL
Nexla's bi-directional connectors can both send data to and receive data from any data system. This means that once a user has created or gained access to a credential for any data system, building any data flow to ingest data from or send data to a location within that data system requires only a few simple steps.
Connecting to Google Cloud SQL
Three Google Cloud SQL connectors are available in Nexla, allowing users to connect to any Cloud SQL instance. This page provides instructions for using the Google Cloud SQL MySQL connector for instances of Cloud SQL used with MySQL databases.
To connect to a different type of Google Cloud SQL instance, see Google Cloud SQL (PostgreSQL) or Google Cloud SQL (SQLServer).
Authentication
This section provides step-by-step instructions for creating a new Cloud SQL MySQL credential that will allow Nexla to authenticate to your Cloud SQL instance.
- To create a new Cloud SQL MySQL credential, after selecting the data source/destination type, click the Add Credential tile to open the Add New Credential overlay.
New Credential Overlay – Cloud SQL MySQL
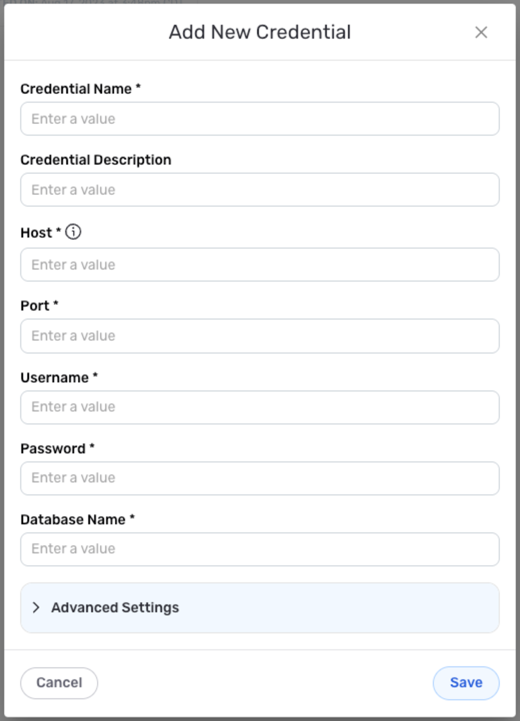
Credential Name & Description
-
Enter a name for the credential in the Credential Name field and a short, meaningful description in the Credential Description field.
Resource DescriptionsResource descriptions should provide information about the resource purpose, data freshness, etc. that can help the owner and other users efficiently understand and utilize the resource.
Authentication Details
- Select the authentication method that will be used to connect to the Cloud SQL instance from the Authentication Type pulldown menu, and follow the corresponding instructions in the box below to configure associated credential settings.
Host – Hostname of the database server (formatted as an IP address or text in the format
company.domain.com)Port – Number of the port that will be used to connect to Cloud SQL
Username – Username for accessing the Cloud SQL instance
Password – Password associated with the Cloud SQL username
Database Name – Name of the Cloud SQL database that will be accessed with this credential
Advanced Settings
For Cloud SQL MySQL credentials, advanced settings are available to configure how Nexla will access the Cloud SQL instance. These settings are optional and can be configured as needed.
- To access advanced settings for the credential, expand the Advanced Settings section at the bottom of the overlay. Instructions for configuring the available connection settings are provided in the box below.
Advanced Credential Settings
Cloud SQL MySQL
- SSH Tunneling
If the Cloud SQL instance is not publicly accessible, Nexla can be configured to connect to the instance via the SSH protocol. When this option is selected, Nexla will connect to a bastion host via SSH, and the database connection will then be provided through the SSH host.
To enable SSH tunneling for Cloud SQL connections with this credential, check the box next to Requires SSH Tunnel for Access?, and enter the following information in the displayed fields:
SSH Tunnel Host – Hostname or IP address of the bastion host running the SSH tunnel server that has access to the database
SSH Tunnel Port – Tunnel bastion host port that will be accessed for connection
Username for Tunnel – SSH username created for Nexla in the bastion host (typically set as
nexla)
Save the Credential
-
Once all of the relevant steps in the above sections have been completed, click the Save button at the bottom of the overlay to save the configured credential.
-
The newly added credential will now appear in a tile on the Authenticate screen during data source/destination creation and can be selected for use with a new data source or destination.
Data Source
To ingest data from a Google Cloud SQL location, follow the instructions in Section 2 of Common Setup for Databases & Data Warehouses.
Data Destination
To send data to a Google Cloud SQL location, follow the instructions in Section 3 of Common Setup for Databases & Data Warehouses.