Query Data with NOVA
NOVA is Nexla's GenAI-powered chatbot that enables users to query their organization's data using natural language. By combining retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with large language models (LLMs), NOVA provides rapid, accurate insights from data across multiple sources, expediting analysis workflows and eliminating the need for complex query languages.
With NOVA, you can directly query your data with questions ranging from simple data lookups to complex analytical queries that span multiple datasets. Whether identifying specific information in lengthy documents, analyzing large datasets for patterns, or connecting information across sources to identify correlations and trends, NOVA translates natural language questions into comprehensive, accurate responses.
How NOVA Works
NOVA uses retrieval-augmented generation to combine the power of search algorithms with the capabilities of large language models. When a query is submitted, NOVA analyzes the selected data—including any available metadata and contextual information—and generates a response based on both the data itself and its contextual relationships.
NOVA maintains the same strict data isolation and access controls valued throughout the Nexla platform, ensuring data integrity and privacy while providing powerful querying capabilities.
Supported Data Sources
NOVA can query detected and transformed Nexsets containing data from three data source types:
-
REST APIs: Queries are constructed using macros, allowing direct interaction with API endpoints.
-
SQL Databases: SQL data sources created using Query Mode, with queries following the format
{query = <SQL query>}—for example,{query = SELECT * FROM account_metrics_daily}. -
Vector Databases: NOVA can query vectorized data stored in vector databases, providing responses based on both the relevant data and its contextual relationships with other data in the database. To prepare data for vector database querying, create a data flow that vectorizes ingested data and sends it to your vector database.
Prerequisites
Before using NOVA, you'll need to create a service key for authentication and ensure your data sources are properly configured in Nexla.
Service Key
A Nexla service key is required to initialize a NOVA querying session. Service keys are forever keys associated with your Nexla account and are used to programmatically access Nexla and obtain a session token.
Account service keys are equivalent to your account password. These keys should be securely stored and treated as highly sensitive information.
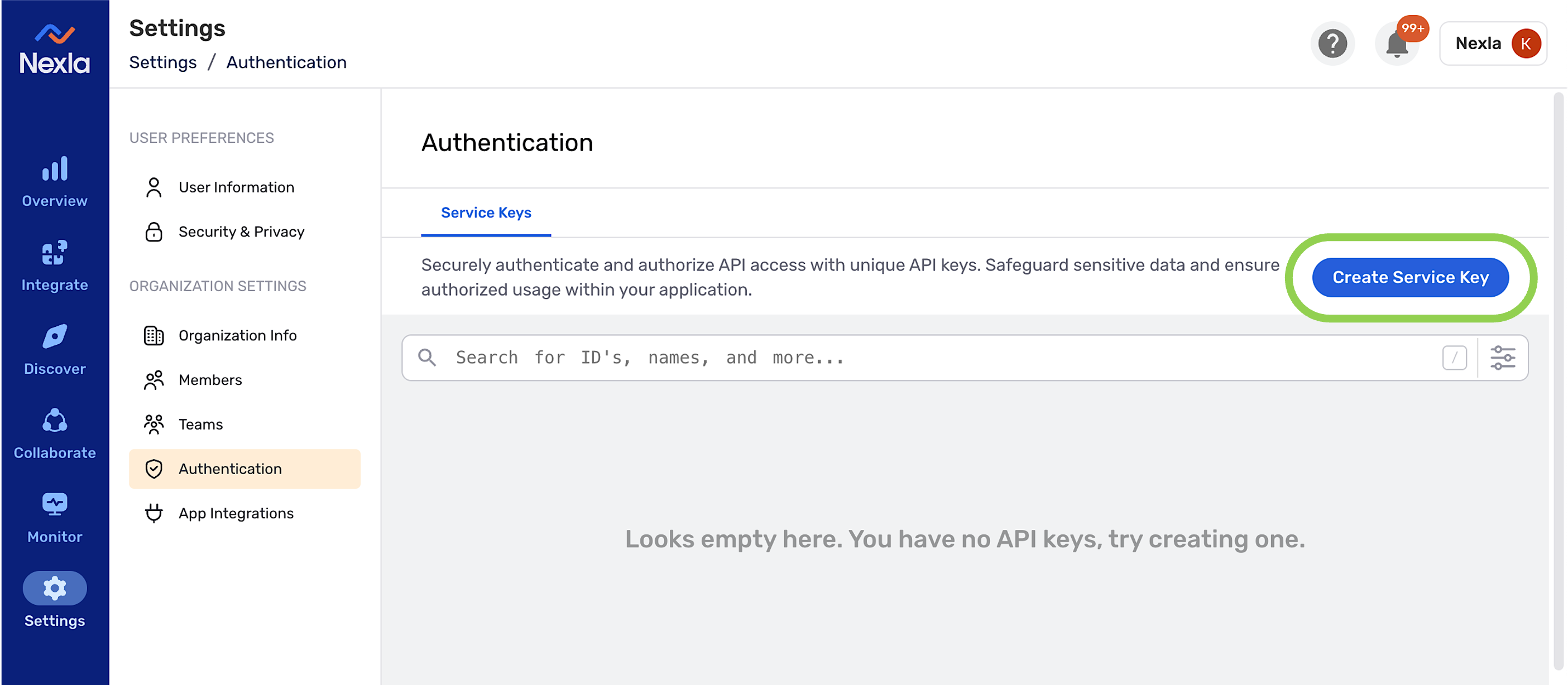
To create a service key:
- In Nexla, navigate to the Settings section, and open the Authentication screen.
- Click the Create Service Key button.
- Copy and securely store the generated service key for use in the NOVA interface.
Data Source Configuration
Before querying data with NOVA, ensure that the data sources you want to query meet the following requirements:
- The vector database, SQL database, or REST API source and associated Nexset(s) must be in active status in a data flow within your account.
- For SQL databases, the source must be created using Query Mode, and the query must follow the format
{query = <SQL query>}—for example,{query = SELECT * FROM account_metrics_daily}.
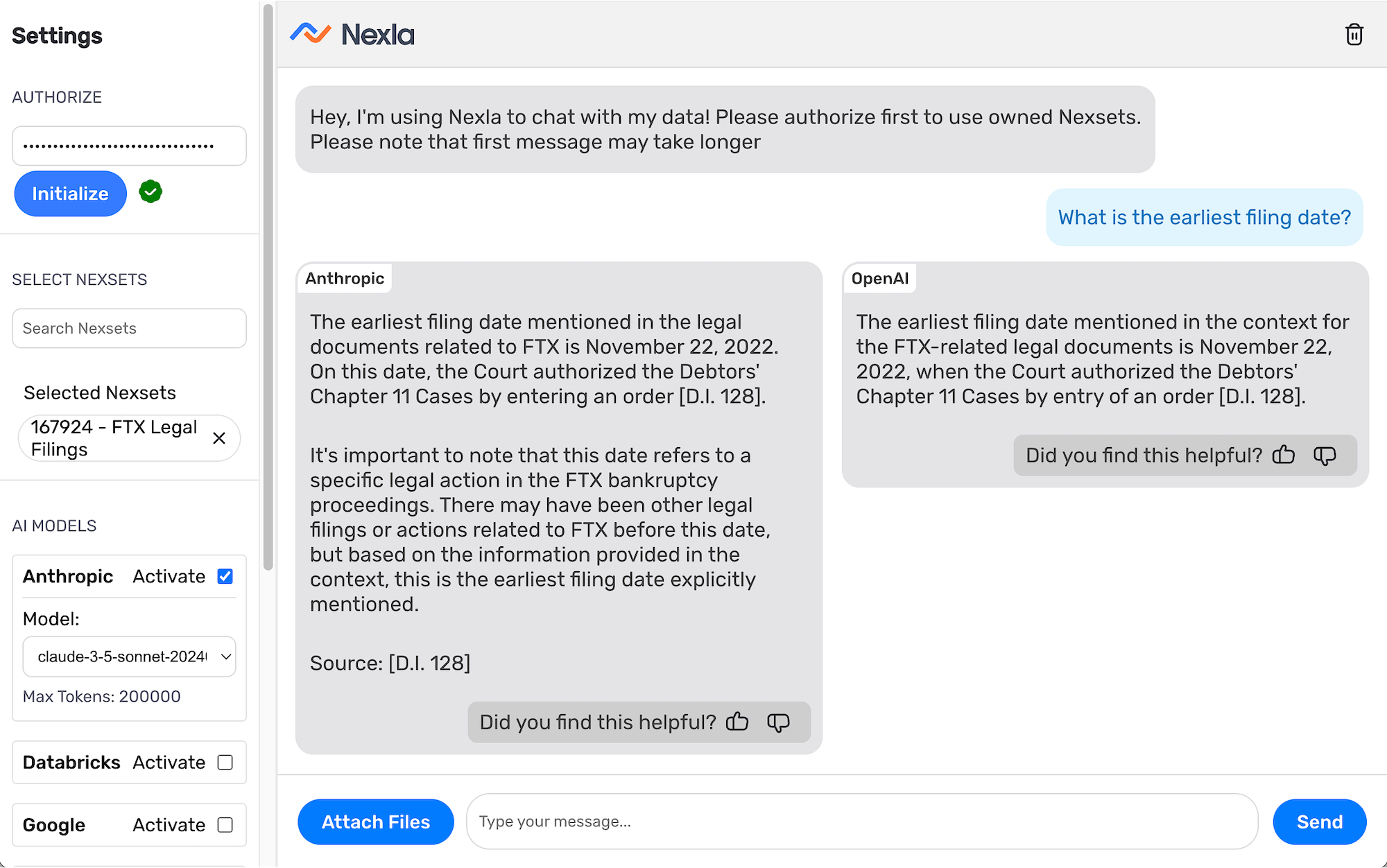
Using NOVA to Query Your Data
To query your data with NOVA, simply initialize your session with a service key, select the Nexsets you want to query, and choose which LLM(s) will generate responses. Then, you can submit queries and receive intelligently formulated, accurate responses from the selected models.
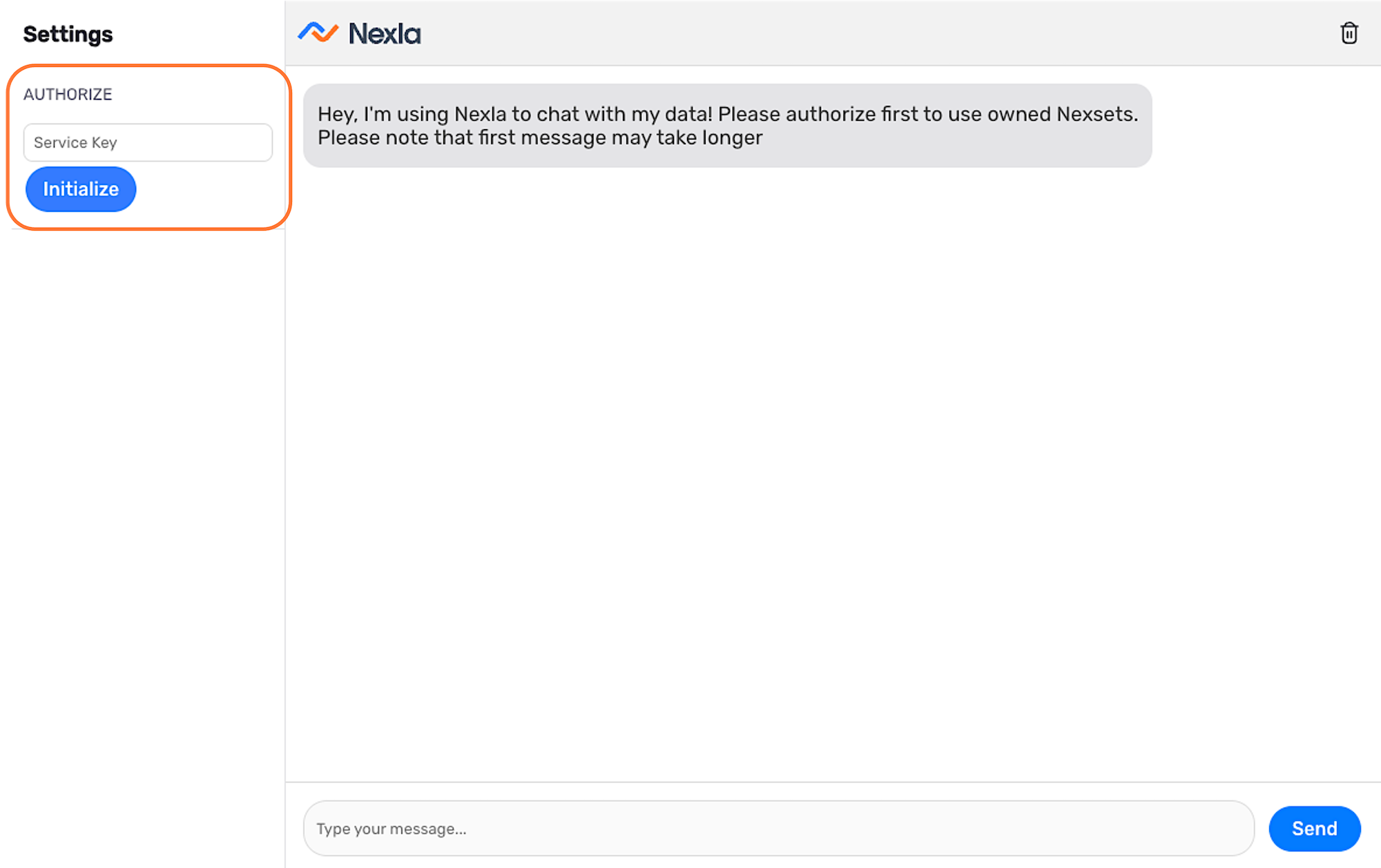
Initialize Your Session
Each NOVA session must be initialized using your account service key.
- Navigate to https://genai.nexla.com/.
- Under Authorize in the left toolbar, paste your account service key into the Service Key field.
- Click Initialize to authorize your account and begin the session.
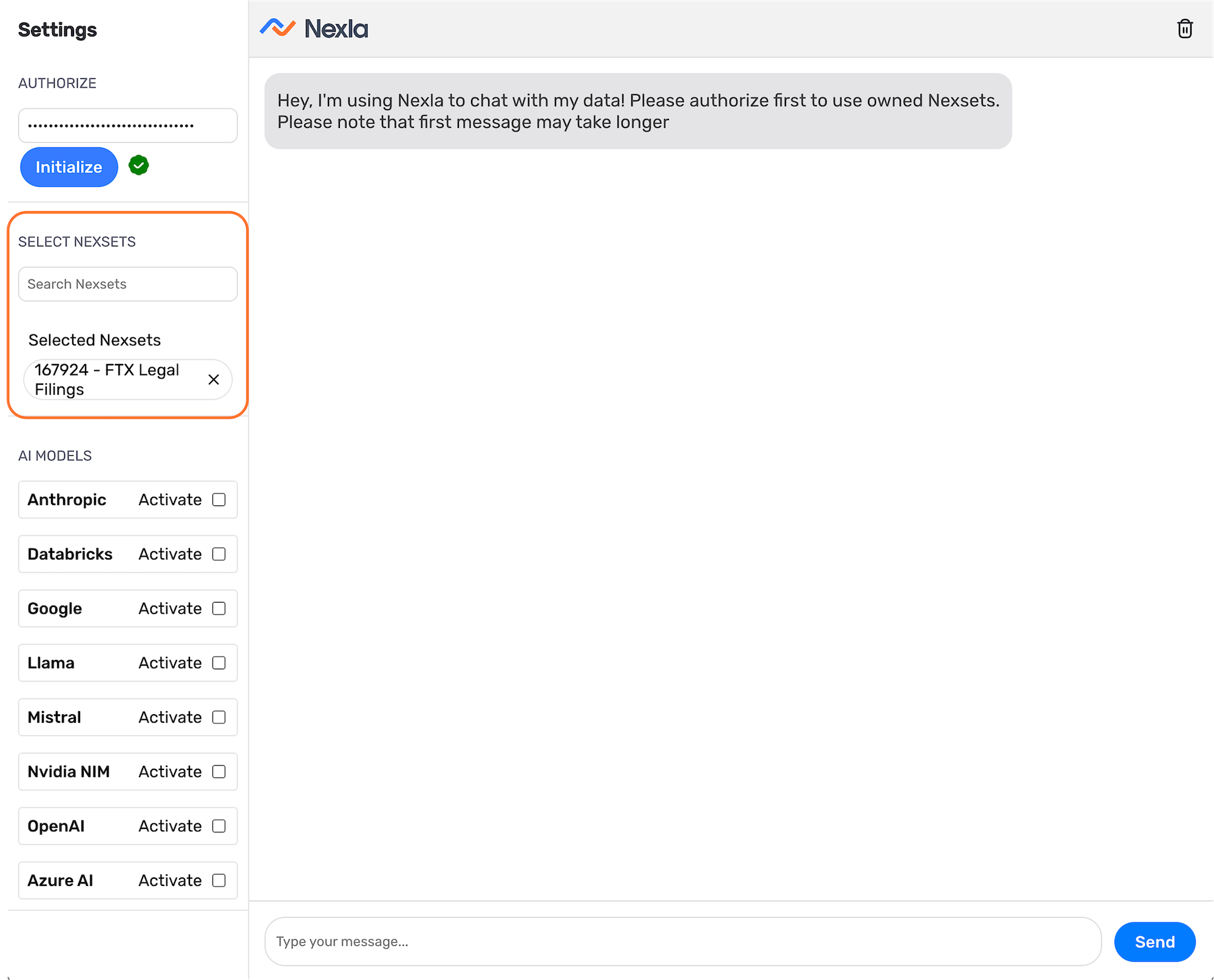
Select the Nexset(s) to Query
NOVA can query one or more Nexsets in a single session, enabling simultaneous queries across multiple data sources and source types.
- Under Select Nexsets in the left toolbar, use the Search Nexsets field to locate the Nexset(s) you want to query. Nexsets can be located by searching with the Nexset ID or the full or partial Nexset name.
- Click on a Nexset in the search results to select it for querying. Selected Nexsets appear under the Selected Nexsets heading.
- To query multiple Nexsets, repeat the search and selection process for each additional Nexset.
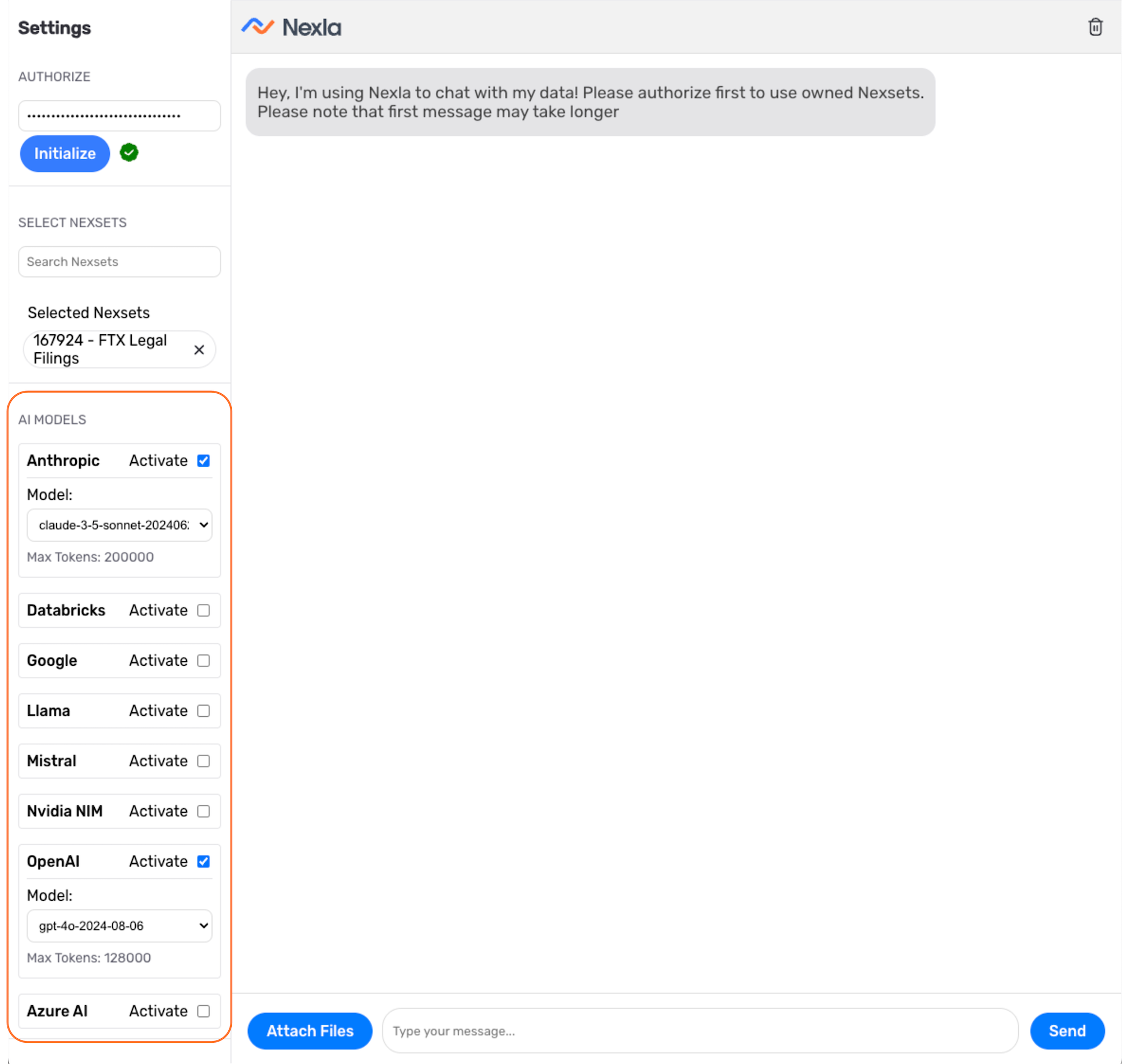
Select the LLM(s)s
NOVA integrates with multiple LLM providers and models, including Google, OpenAI, Databricks, Anthropic, and more. You can select one or more LLM providers and versions to generate responses during your session. Custom LLMs can also be integrated using the REST API connector.
When selecting LLMs, consider applicable rate limits, which vary among models. Larger models such as GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 typically limit users to fewer requests per day (approximately 50), while smaller models such as GPT-4o mini allow more requests per day (approximately 200). Request counts are typically reset daily based on your service key.
- Check the Activate box next to each LLM provider you want to use.
- For each selected provider, use the pulldown menu to select the specific model that will be used to analyze the data and generate responses.
Submit Queries
Once Nexsets and LLMs are selected, you can begin querying your data.
-
Type your query into the chat text field at the bottom of the window, and press Enter or click Send to submit the query.
-
Each selected LLM will receive the query, analyze the selected data and provide a response in the chat window.
-
You can continue the conversation to refine your results, obtain more information, etc. by submitting additional queries.
When querying Nexsets from REST API and SQL database sources, responses are based on the Nexset data and included contextual information. With vector database sources, responses are based on vector database searches that include contextual information from nearest neighbors and related vectors.
Query Best Practices
To obtain the most accurate and useful responses from NOVA, structure your queries with specificity and relevant context.
Be specific: Include relevant details such as date ranges, data attributes, or specific parameters. Rather than asking "What are the sales figures?", ask "What are the sales figures for Q3 2024 in the Northeast region?"
Provide context: When appropriate, specify what information should be included or excluded from responses. For example, "Show me customer feedback excluding automated survey responses."
Use follow-up queries: Build on previous responses to refine results or explore different aspects of the data. NOVA maintains session context, allowing for conversational query refinement.
Leverage multiple Nexsets: When querying across multiple data sources, specify any relationships or connections you're investigating to help NOVA provide comprehensive insights.
Related Resources
- For a step-by-step tutorial on using NOVA with example data and queries, see Querying Data Using GenAI.
- To learn how to prepare text data for vector database querying, see Sending Text Data to Vector Databases.
- For information on creating RAG-powered data flows for application integration, see RAG Data Flows.